The causes of a flat foot or a hollow foot are multiple :
- Genetical
- Muscular: coordination disorder (proprioception) and/or muscle weakness
- Postural: the foot adapts itself to an ascending problem (jaw, eye, vestibule). It is placed in a position necessary to ensure a perfect body balance in its overall deformity.
- Related to a bad shoe or bad soles used in the past. Man was born barefoot, yet he lives with shoes.
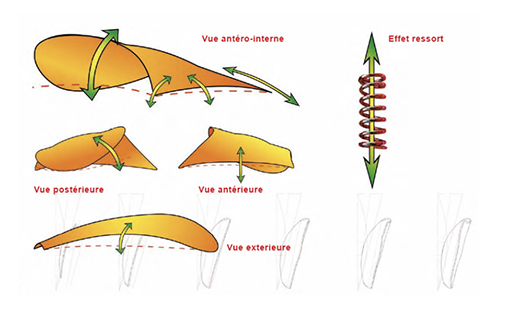
The Kinepod, Orthes and Tedop plantar activators are the only dynamic insoles with active properties. They correct the foot while giving it the greatest possible freedom of movement. By functioning as a proprioceptive guide, they allow the foot to achieve normal functionality.Plantar activators have the particularity of guiding the foot, on the one hand, in a movement of inverting force at the beginning and at the end of the step, and at the other hand in a movement of everting force in the middle of the step (respect of joint physiology). They tend to inform the body and its neurological system of the correct position of the foot joints. Without being aggressive, the plantar activators will prevent excess eversion and inversion while neurologically stimulating the skin, joint and muscle receptors of the foot.
Plantar activators have the virtue of informing the brain of the ‘ideal’ positioning of the foot, while rehabilitating the muscles of the lower limb and trunk in perfect timing. Through this mechanism, the body is in the long run capable of assuming independently a joint and muscle physiology in movement and in postural static.
By means of an innovative system of adding elements and elastic straps, the plantar activators have the advantage of adapting to each pathology and, above all, to their evolution.
The Kinepod, Orthes and Tedop plantar activators are currently the only medical insoles capable of rehabilitating both walking and posture.
WALKING WITHOUT A PLANTAR ACTIVATOR
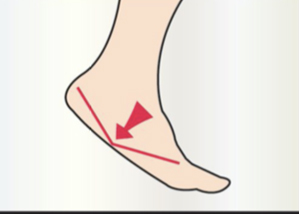
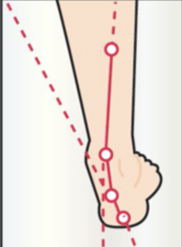
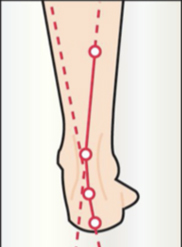
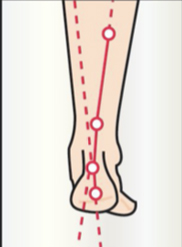
WALKING WITH A FOOT ACTIVATOR
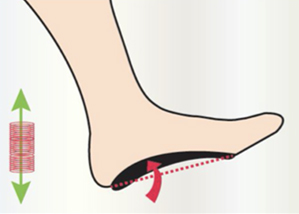
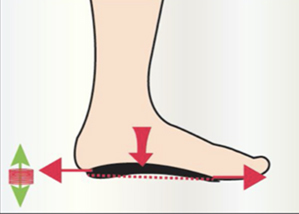
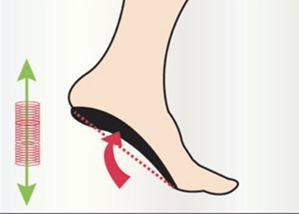
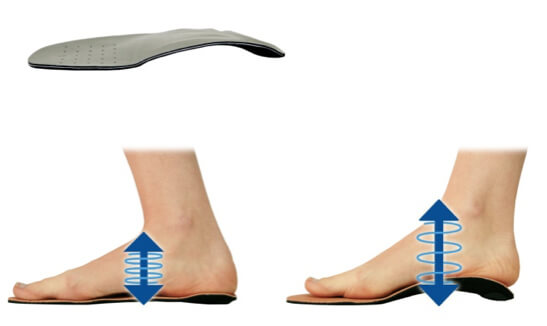
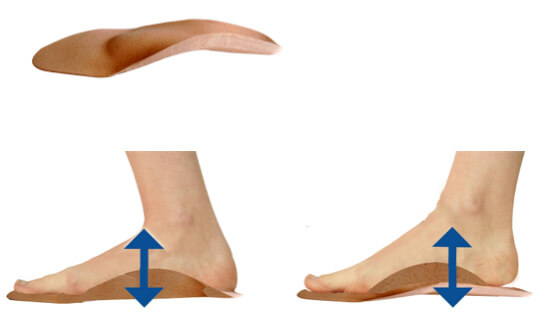
The plantar activator guides the foot in physiological rotations (inversion-eversion-inversion) which steer the lower limb and pelvis during walking. The exercise is comparable to a rider learning to ride a horse. During the trot, he is jolted to pieces, but gradually takes the rhythm of the horse and follows his movement. The foot activator has the same function. Initially, it pushes the foot (feels like a spring), but gradually the foot will take over and be able to recreate this physiological movement on his own.
During walking, the foot performs 2 main steps :
- Energy absorption = cushioning
- Energy restitution = energy saving in propulsion
The plantar activator perfectly fulfils these 2 functions.
The plantar activator is stimulating because it forces the whole body to work through the rotations it imposes on the foot and the lower limb (in an ascending chain).
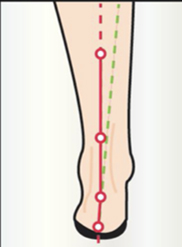
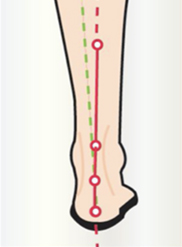
From a very young age, parents should be advised in choosing physiological footwear. An assessment from the age of 4 years is recommended in order to analyse the functioning of the foot using the ‘OPS-Clinic’ software. It is important to know that it takes until the age of 8 years for the child's foot to be perfectly straight. It has an eversion of 7-8 degrees at 2 years old and reaches normality of 0° at 8 years old.
The plantar activator stimulates the proprioceptive sensors of the foot via the skin, muscles, tendons and joints.
It acts on a better awakening of the foot as a whole and ensures that it functions better as foundation of the body.
In an ascending articular chain, the foot favours rotations which force the lower limb and the pelvis to modify their movement. The posture can thus be in better balance.
In movement, the foot works like the shock absorbers and tyres of a car :
The covering of the sole and the shoe are the tyre. It protects the rims which are the bones.
The active carbonesate corrector base is the shock absorber.
Thanks to our shock absorbers, just like a 4 X 4 vehicle, our feet can adapt to unstable terrain while keeping the posture in balance (the frame of the car). Shock absorbers also help to absorb excessive shocks and save energy over long distances. Symmetry between the shock absorbers is essential to avoid parallelism problems.
The plantar activator can be modified by adding reinforcement to inhibit or stimulate the foot muscles.
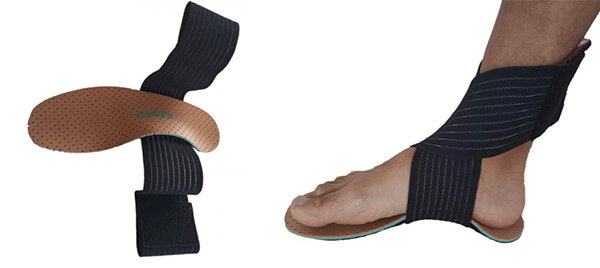
It can also be coupled with straps to act directly on the ankle and all the extrinsic muscles of the foot. The straps can also be used for stimulation or inhibition depending on their placement and tension.
This modulable aspect is very interesting for kinesitherapy/physiotherapy rehabilitation.
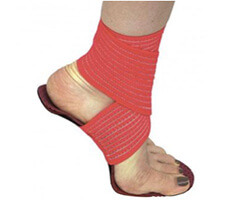
The injured external ligament can be relieved by an active sole combined with a double strap. The external strap runs over the bridge and hooks onto the ankle. It is tighter than the inner strap and promotes eversion.
During the healing phase (10-15 days), this higher external tension is maintained to allow the ligament to heal and prevent the foot from inadvertently going into inversion (which would again damage the ligament).
Afterwards, the tension can be balanced until the patient completely abandons the straps.
However, he will keep them for his physiotherapy rehabilitation. The physiotherapist will tension the inner strap in order to stimulate the long peroneal muscle during exercises. Placing the ligament under tension will stimulate its proprioceptive sensors (i.e. a ligament only responds proprioceptively when it is under tension). However, a sprain must be avoided, which is why it is necessary to maintain an opposite tension with the external strap.
The foot can be trained for 15-20 minutes by stimulating the peroneal muscles and stimulating proprioceptive sensors of the ligaments. The kinesitherapist/physiotherapist can also amplify the position of the foot by adding reinforcements to the insole. These will force the foot to position itself in inversion in order to overload the peroneal muscles.
The work must be done progressively and spread over several sessions.
The processing of sensory information by the brain, through automatic regulation, is done 4 to 11 times per second in a 24-hour operation (depending on the sensors and their reactivity).
Wearing a soft shoe promotes a ‘comfort effect’ that inhibits the proprioceptive sensors. They no longer perceive the reality of contact with the ground since it is camouflaged by the foam of the shoe. A foot sensor that has to react 11 times / sec., 24 hours a day, in normal circumstances, will only react 2 times / sec. if the foot is constantly in a soft shoe. This will reduce responsiveness and proprioceptive coordination.
A cushioning shoe also has the disadvantage of making the foot muscles lazy. They no longer need to put pressure on the joints so that the foot twists and becomes springy. What's the point of making an effort if there is already help available? The human body is lazy by nature. It always chooses the easy way out. This also explains how a foot can become hypotonic and even deform in the long run.

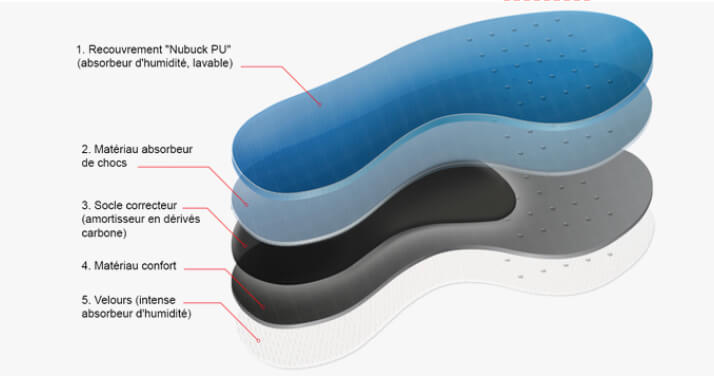






All the products of the OPS Clinic are made by 3D thermo-injection. This system is much more complex and expensive than thermoforming. It is impossible to obtain such a precise result in a traditional way.
Materials such as carbonesate (used in the aerospace industry) and silicemed are of the latest generation and very difficult to process (which justifies the complexity of the manufacturing process).
The production machines are: manufacture machines (to create the moulds) and thermo-injection machines (to inject the carbonesate or liquefied silicemed into the mould).